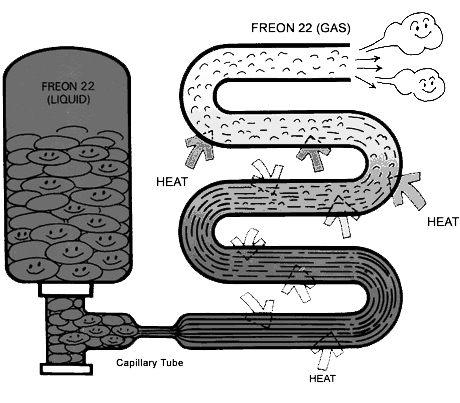
When a liquid evaporates or boils (change of state) heat is absorbed by the liquid. If air is the source of heat, the air will be cooled by the loss of heat.
An air conditioner evaporates refrigerant contained in the indoor coil and absorbes heat from air passing over the coil. This cooler air is then returned to the room.
Freon 22 is generally used as refrigerant for residential use and light commercial use air conditioners. Freon 22 has superior characteristics as refrigerant such as low evaporating and condensation temperature, high stability and low corrosivity for metals.
The figure below shows the flow of Freon 22 which evaporates and flows inside a tube while absorbing heat from the surrounding air. In other words it shows how heat is transferred from one location to another location.
In reality an airconditioner is designed with a refrigeration cycle that consists of heat being absorbed by the refrigerant as it evaporates inside a room. This gas is then pumped by the compressor to the outdoor coil where it is put under high pressure which causes the refrigerant to condense (change state) as it gives up its heat to the air passing over the coil and returns to the indoor coil as a liquid to repeat the process.