

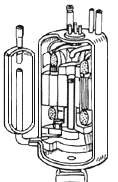
 (COMP) Compresses low temperature, low pressure gas to high temperature, high pressure gas. This conversion changes the boiling point which allows for easy heat removal and condensation of the gas. The compressor is the heart or pump of the system causing the refrigerant to flow.
(COMP) Compresses low temperature, low pressure gas to high temperature, high pressure gas. This conversion changes the boiling point which allows for easy heat removal and condensation of the gas. The compressor is the heart or pump of the system causing the refrigerant to flow.
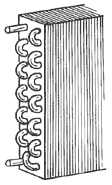 The section that receives high temperature, high pressure gas from the compressor. Air flowing across the coils removes heat from the refrigerant which condenses into a liquid. (Water cooled type uses water instead of air to remove heat.)
The section that receives high temperature, high pressure gas from the compressor. Air flowing across the coils removes heat from the refrigerant which condenses into a liquid. (Water cooled type uses water instead of air to remove heat.)
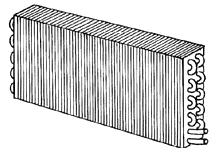 The refrigerant evaporates in the evaporator, absorbs heat from the surrounding air and produces cold air.
The refrigerant evaporates in the evaporator, absorbs heat from the surrounding air and produces cold air.
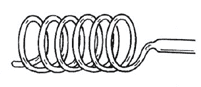 A fixed restriction place in the line to allow compress to build high pressure and due to its inside diameter (1.0 to 2.0 mm or 0.04 to 0.08 inches) and length (1 to 2 m or 3.3 to 6.6 ft.) it meters the correct amount of refrigerant into the evaporator.
A fixed restriction place in the line to allow compress to build high pressure and due to its inside diameter (1.0 to 2.0 mm or 0.04 to 0.08 inches) and length (1 to 2 m or 3.3 to 6.6 ft.) it meters the correct amount of refrigerant into the evaporator.
Components necessary to operate specific items at specific times to coordinate the functions.
 Pulls room air into unit and forces it through the evaporator and distributes cooler air into the room. Fan at riqht etc.
Pulls room air into unit and forces it through the evaporator and distributes cooler air into the room. Fan at riqht etc.
 Outdoor fan Forces air through the condenser, removing heat and cooling the refrigerant.
Outdoor fan Forces air through the condenser, removing heat and cooling the refrigerant.



